With the growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy solutions, the demand for lithium-ion batteries has surged. This shift toward sustainable energy has also brought battery recycling into the spotlight, especially in countries like India. Historically, the Battery (Management and Handling) Rules, 2001 governed the disposal of lead-acid batteries, but these regulations did not address the complexities of lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles.
In response, India’s Ministry of Environment, Forestry and Climate Change (MOEFCC) unveiled a draft of the Battery Waste Management Rules in February 2020. Following feedback from industry stakeholders, a revised version was published on August 24, 2022.
These updated rules apply to:
- Producers, dealers, consumers, and entities involved in the collection, segregation, transportation, refurbishment, and recycling of waste batteries.
- All types of batteries, regardless of their chemistry, shape, weight, material composition, or use.
Key Features of the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022
1. Reduced Dependence on Virgin Resources
The rules emphasize incorporating a specified proportion of recycled materials in new battery production. This approach minimizes the need for raw material extraction, conserving natural resources.
2. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Under EPR guidelines:
- Battery manufacturers, including importers, are responsible for the collection, recycling, and refurbishment of used batteries.
- Disposal through landfills or incineration is strictly forbidden. Instead, waste batteries must be processed through recycling or refurbishment.
- Producers can either handle these tasks themselves or authorize third parties to ensure compliance.
“The polluter pays” principle holds producers accountable for meeting their EPR obligations. Non-compliance results in environmental compensation penalties.
3. Environmental Compensation Fund
Funds collected from penalties are allocated to improve the collection, refurbishment, and recycling of improperly managed waste batteries.
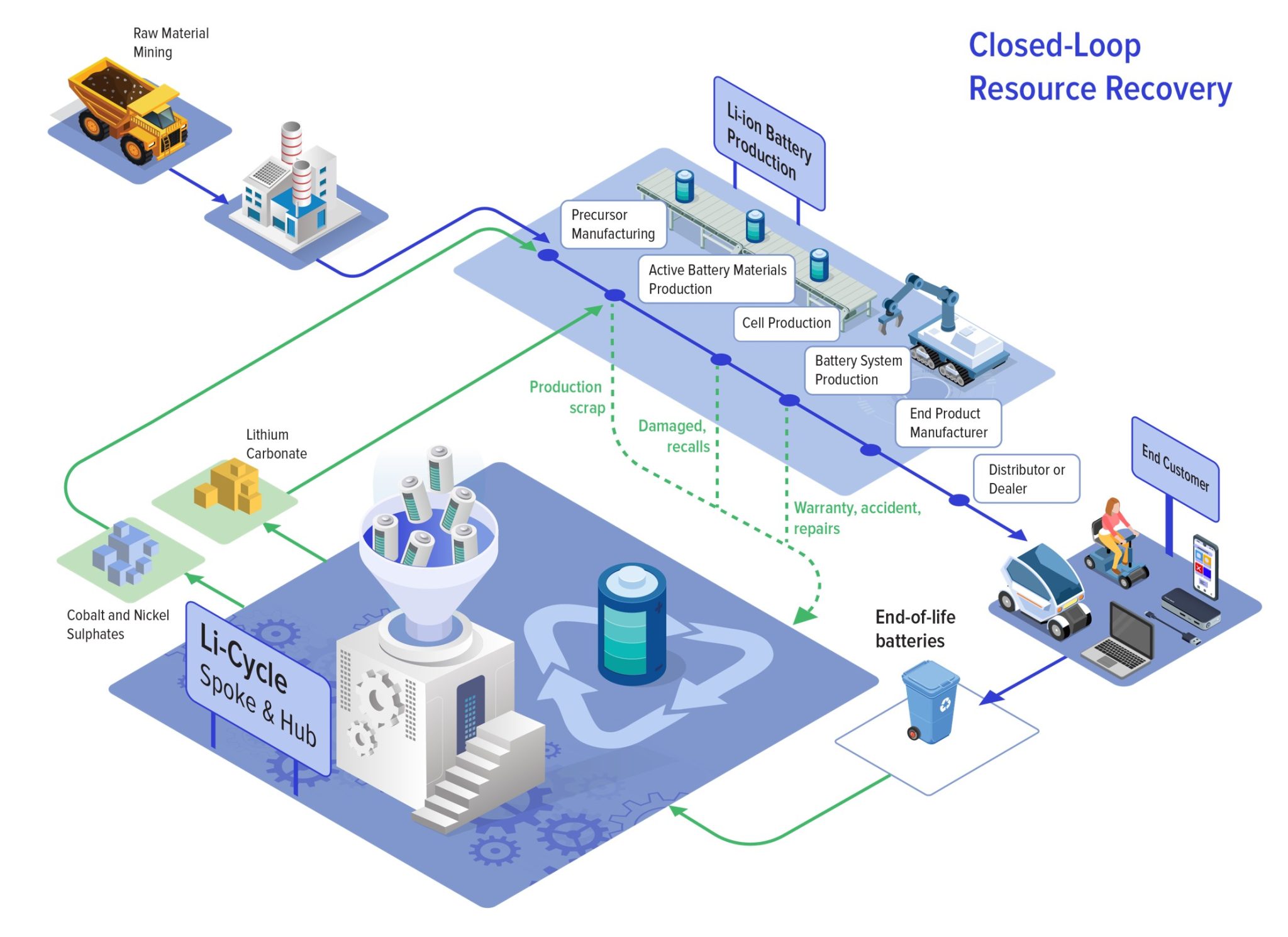
4. Centralized Online Platform
The rules mandate the creation of a centralized web portal to:
- Facilitate the exchange of EPR certificates between producers and recyclers.
- Streamline processes like registration, reporting, and auditing to enhance compliance.
Economic and Environmental Merits of Recycling Lithium-Ion Batteries
Cost-Efficiency
- Disassembling used batteries to recover parts is far less expensive than manufacturing entirely new components.
- Recycling retrieves valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, reducing the environmental footprint and protecting natural habitats.
Environmental Impact
- Recycling significantly curtails pollution and energy consumption compared to raw material extraction.
- Proper recycling prevents harmful substances from seeping into soil and water, safeguarding ecosystems.
- Reusing old EV batteries for stationary energy storage can meet up to 65% of storage needs and achieve 30-70% cost savings compared to new batteries within the next decade.
Challenges in Battery Recycling
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Lack of infrastructure | Ineffective collection and recycling, especially in remote regions. |
| Diverse battery designs | Complicates the establishment of universally equipped recycling facilities. |
| Large EV battery packs | Increases disassembly complexity and risks. |
| Cost of salvaging materials | Retrieving certain elements like lithium is more expensive than mining them. |
| Limited current supply | Most EV batteries are yet to reach their recycling phase, creating a shortage for large-scale facilities. |
Despite these obstacles, battery recycling strengthens supply chain security, reduces dependency on raw materials, and fosters social and environmental sustainability.
Broader Benefits of Recycling
Job Creation and Economic Growth
Recycling initiatives generate employment opportunities at multiple levels, boosting local economies and community engagement.
Community Development
Establishing recycling centers in underserved regions promotes responsible waste management and raises environmental awareness.
Accessible Energy Solutions
Recycled battery materials pave the way for affordable energy storage, particularly in remote areas, improving living standards and energy accessibility.
The Takeaway
As consumers, we hold the power to influence change by choosing responsible disposal methods and supporting battery recycling efforts. By doing so, we contribute to a greener, more sustainable future, where our actions echo a legacy of renewal, resilience, and responsibility.
“Together, we can energize a world driven by sustainability.”



